Computer Architecture and Organization (CT 211) - Exam
THE UNIVERSITY OF DODOMA
COLLEGE OF INFORMATICS AND VIRTUAL EDUCATION
SCHOOL OF INFORMATICS
UNDERGRADUATE UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS
FIRST SEMESTER 2017/2018
CN 210: COMPUTER ARCHITECTURE AND ORGANIZATION
Date: 26th February, 2018
Time allocated: 3 Hours
Instructions:
- This examination consists of Two Sections A and B. Section A (40 marks) and Section B (60 marks).
- Answer ALL questions from Section A and any THREE from Section B.
- All University of Dodoma Examination Regulations Apply.
SECTION A (40 Marks)
Question One
a) List and briefly define the main structural components of a processor. (4 Marks)
b) As a computer architect at Computrax Company Limited, Christina has decided to include a multiply instruction in an instruction set for a new computer family. However, Christina is bothered on whether that multiply instruction will be implemented by a special multiply unit or by a mechanism that makes repeated use of an add unit of a new computer system.
i. Briefly explain whether Christina is faced with an architectural or organizational decision. (2 Marks)
ii. Based on your answer in b (i) above, assist Christina by providing at least four (4) factors that she can use in making decision. (4 Marks)
Question Two
a) Name three different ways which the signed integers can be represented in digital computers and explain the differences. (4 Marks)
b) Convert the following:
i. 275.4375₁₀ to octal (3 Marks)
ii. 514.7₁₀ to binary (3 Marks)
Question Three
a) Illustrate the memory hierarchy and its components and define the parameters which characterize the arrangement in that hierarchy. (5 Marks)
b) What architectural solution does the memory hierarchy provide to the performance of computer system? Briefly explain how? (5 Marks)
Question Four
a) What are the RISC design principles and how can they be achieved? (5 Marks)
b) Write the main characteristics RISC Architecture. (5 Marks)
SECTION B (60 Marks)
Question Five
a) Represent the decimal values 26, -123 as signed, 10-bit numbers using each of the following binary formats: (2 Marks Each)
i. 1’s complement
ii. 2’s complement
b) Add the following using one’s complement arithmetic using 8-bit binary format: (4 Marks Each)
I. 23 and -9
II. -46 and -25
c) Convert each of the following decimal numbers to their IEEE single precision floating-point counterparts: (4 Marks Each)
i. 0.92
ii. 5.3125
Question Six
a) Write three-address, two-address, and one-address programs to compute the function A = (B-C) * (D-E).
(6 Marks)
b) Briefly explain the following with examples: (6 Marks)
i. Direct addressing mode
ii. Indirect addressing mode
iii. Index addressing mode
c) Suppose we have the instruction Load 1000. Given that memory and register R1 contain the values as shown in Figure 1:
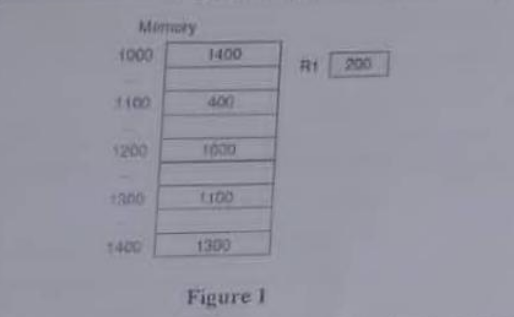 Figure 1
Figure 1
Assuming R1 is implied in the indexed addressing mode, determine the actual value loaded into the accumulator and fill in the table 1 for the different addressing modes: (8 Marks)
| Mode | Value Loaded into AC |
|---|---|
| Immediate | |
| Direct | |
| Indirect | |
| Indexed |
Table 1
Question Seven
a) Explain the concept of locality of reference and state its importance to memory systems. (5 Marks)
b) For an associative cache, a main memory address is viewed as consisting of two fields. List and define the two fields. (5 Marks)
c) Suppose a computer using fully associative cache has 2²⁴ words of main memory and a cache of 128 blocks, where each cache block contains 64 words.
i. How many blocks of main memory are there? (3 Marks)
ii. What is the format of a memory address as seen by the cache, that is, what are the sizes of the tag and word fields? (3 Marks)
iii. To which cache block will the memory reference 01D872₁₆ map? (4 Marks)
Question Eight
a) Briefly describe the following:
i. Pipeline stall due to instruction dependency (5 Marks)
ii. Pipeline stall due to data dependency (5 Marks)
END OF EXAMINATION PAPER