Computer Networking Protocols - Exam
THE UNIVERSITY OF DODOMA
OFFICE OF THE DEPUTY VICE CHANCELLOR ACADEMIC, RESEARCH AND CONSULTANCY
COLLEGE OF INFORMATICS AND VIRTUAL EDUCATION
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
End of Semester One University Examination for the 2019/2020 Academic Year
Course Name: Computer Networking Protocols
Paper Code Number: CN 211
Date of Examination:
Time: 11:45-14:45
Duration: 3 Hours
Venue(s): FL2, LRB 105, 106, 004C, 004D, 101&102
Sitting Programme(s): BSc. CSDFE2, HIS2, CNISE2, DCBE2, TE2, CE2, SE2, BIS2, SE3, CS2, CS3, CNISE3, TE3&CE3
SECTION A: (40 MARKS)
Question One
a. How is Internet Protocol (IP) similar and dissimilar to User Datagram Protocol (UDP)?
(4 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Similarities:
- Both are connectionless protocols
- Both provide best-effort delivery without guarantees
- Both operate at different layers but share similar datagram structure
- Both can experience packet loss without recovery mechanisms
Dissimilarities:
- Layer: IP operates at Network Layer (Layer 3), UDP at Transport Layer (Layer 4)
- Function: IP handles host-to-host delivery, UDP handles process-to-process delivery
- Ports: UDP uses port numbers, IP does not
- Checksum: UDP has optional checksum, IP has header checksum
- Protocol Field: IP header identifies upper layer protocol (UDP=17)
b. Write similarities and dissimilarities between BOOTP Protocol and Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP).
(6 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Similarities:
- Both provide automatic IP address assignment
- Both use UDP ports 67 (server) and 68 (client)
- Both can provide additional network configuration parameters
- Both use client-server architecture
Dissimilarities:
- Lease Time: DHCP supports temporary leases, BOOTP uses permanent assignments
- Configuration: DHCP can provide all TCP/IP configuration, BOOTP mainly provides IP address
- Dynamic Allocation: DHCP supports dynamic allocation, BOOTP is mostly static
- Backward Compatibility: DHCP is backward compatible with BOOTP
- Message Types: DHCP has more message types for flexibility
- Relay Agents: Both support relay agents but DHCP is more efficient
c. With at least five reasons, state how TCP is different from UDP.
(5 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
TCP vs UDP Differences:
- Connection: TCP is connection-oriented (3-way handshake), UDP is connectionless
- Reliability: TCP guarantees delivery with ACKs and retransmissions, UDP provides best-effort
- Ordering: TCP maintains packet sequence, UDP does not guarantee order
- Flow Control: TCP implements sliding window mechanism, UDP has no flow control
- Congestion Control: TCP adapts to network congestion, UDP has no congestion control
- Header Size: TCP header (20-60 bytes) is larger than UDP header (8 bytes)
- Speed: UDP is faster due to minimal overhead, TCP is slower but reliable
💡 Question Two
Write short notes on the following:
(1 Mark Each)
a. Best-effort protocol
Answer (Click to show)
Best-effort Protocol:
- Provides no guarantees of delivery, order, or timing
- No error recovery or retransmission mechanisms
- Examples: IP, UDP
- Suitable for real-time applications where timeliness matters more than reliability
b. Stateless protocol
Answer (Click to show)
Stateless Protocol:
- Each request is independent and contains all necessary information
- Server doesn’t maintain session information between requests
- Examples: HTTP, IP
- Advantages: Scalability, simplicity
- Disadvantages: May require redundant information in each request
c. TCP Sequence numbers
Answer (Click to show)
TCP Sequence Numbers:
- 32-bit numbers that identify each byte of data
- Ensure proper ordering of segments
- Enable duplicate detection and retransmission
- Initial sequence number (ISN) randomly chosen during handshake
d. Three-way handshake
Answer (Click to show)
Three-way Handshake:
- TCP connection establishment process
- Step 1: SYN from client to server
- Step 2: SYN-ACK from server to client
- Step 3: ACK from client to server
- Purpose: Synchronize sequence numbers, establish connection parameters
e. Windowing
Answer (Click to show)
Windowing:
- Flow control mechanism in TCP
- Receiver advertises window size indicating available buffer space
- Prevents sender from overwhelming receiver
- Dynamic adjustment based on network conditions and receiver capacity
Question Three
Short answer questions:
(1 Mark Each)
a. ______ is a protocol behind commands used to establish connectivity problems and paths to remote hosts.
Answer (Click to show)
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol)
b. ______ field in the IP Packet prevents the packet from looping forever in the Internet.
Answer (Click to show)
TTL (Time to Live)
c. ICMP’s ______ messages were meant to relieve congestions in the network by asking senders to reduce the rate at which they are sending data. This idea is counter-productive because the messages also contribute to congestion and there is no way of informing sending devices that the congestion has been relieved.
Answer (Click to show)
Source Quench
d. ______ is a protocol used to address challenges associated with fragmentation by establishing the minimum Maximum Transfer Units (MTUs) of various links between source and destination before attempting to send data.
Answer (Click to show)
Path MTU Discovery
e. IPv6 addresses have ______ octets.
Answer (Click to show)
16 octets (128 bits = 16 bytes)
Question Four
Map each component/issue to the most appropriate layer of the OSI model:
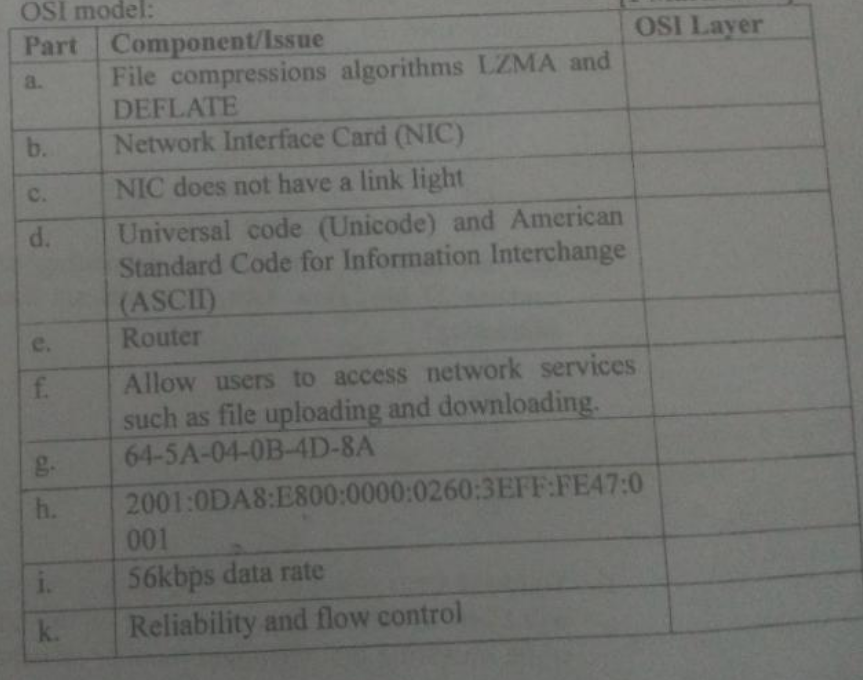
Answer (Click to show)
Component/Issue OSI Layer a. File compressions algorithms LZMA and DEFLATE Presentation Layer b. Network Interface Card (NIC) Physical Layer c. NIC does not have a link light Physical Layer d. Universal code (Unicode) and ASCII Presentation Layer e. Router Network Layer f. Allow users to access network services Application Layer g. 64-5A-04-0B-4D-8A Data Link Layer h. 2001:0DA8:E800:0000:0260:3EFF:FE47:0001 Network Layer i. 56kbps data rate Physical Layer k. Reliability and flow control Transport Layer
Question Five - Multiple Choice
(0.5 Mark Each)
a. Which one of the following is not an address reserved for private networking according to RFC 1918?
- A) 10.10.255.255
- B) 172.16.100.0
- C) 192.168.16.100
- D) 196.128.10.254
- E) 192.168.16.200
Answer (Click to show)
D) 196.128.10.254
- RFC 1918 private addresses: 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12, 192.168.0.0/16
- 196.128.10.254 is a public IP address
b. Which one of the following subnet mask is most often implemented on WAN point-to-point serial links with VLSM?
- A) 255.255.255.252
- B) 255.255.255.254
- C) 255.255.255.248
- D) 255.255.255.240
- E) 255.255.255.0
Answer (Click to show)
A) 255.255.255.252
- /30 mask provides 2 usable hosts
- Perfect for point-to-point WAN links (2 routers)
c. You are using a subnet mask submitting scheme that contains 27 bits. How many host bits are there for host addressing?
- A) 1
- B) 2
- C) 4
- D) 5
- E) 3
Answer (Click to show)
D) 5
- Total bits: 32
- Network bits: 27
- Host bits: 32 - 27 = 5
d. You have been asked to come up with a subnet mask that will allow all three web servers to be on the same network while providing the maximum number of subnets. Which network address and subnet mask meet this requirement?
- A) 192.168.252.0 255.255.255.252
- B) 192.168.252.8 255.255.255.248
- C) 192.168.252.8 255.255.255.252
- D) 192.168.252.16 255.255.255.240
- E) 192.168.252.16 255.255.255.252
Answer (Click to show)
B) 192.168.252.8 255.255.255.248
- /29 mask provides 6 usable hosts (enough for 3 servers)
- Allows maximum subnets while meeting host requirement
e. Which of the following is the corresponding port number for HTTPS?
- A) 80
- B) 8080
- C) 441
- D) 443
- E) 21
Answer (Click to show)
D) 443
- HTTP: Port 80
- HTTPS: Port 443
f. Domain Name Service is associated with which of the following well-known port numbers?
- A) 20 and 21
- B) 23
- C) 25
- D) 53
- E) 80
Answer (Click to show)
D) 53
- DNS uses port 53 for both TCP and UDP
g. Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) Server listens on port:
- A) 53
- B) 80
- C) 67
- D) 68
- E) 23
Answer (Click to show)
C) 67
- DHCP Server: Port 67
- DHCP Client: Port 68
h. What port number is used when downloading an email from the Mail server to your client computer?
- A) 25
- B) 110
- C) 23
- D) 21
- E) 80
Answer (Click to show)
B) 110
- POP3 uses port 110 for email retrieval
- SMTP (sending) uses port 25
i. When a user is opening a website such as www.udom.ac.tr from his/her computer, the source port number is automatically assigned by the computer’s Operating System from the following range:
- A) 0-1023
- B) 1024-49151
- C) 49152-65,535
- D) 0-49151
- E) 0-65,535
Answer (Click to show)
B) 1024-49151
- Well-known ports: 0-1023
- Registered ports: 1024-49151
- Dynamic/private ports: 49152-65535
j. Which of the following is a unicast MAC Address?
- A) FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF
- B) 65-5A-04-0C-4E-82
- C) 27-AA-04-0C-4E-85
- D) 59-33-22-0C-4E-86
- E) 64-5A-04-0B-4D-8A
Answer (Click to show)
B) 65-5A-04-0C-4E-82
- Unicast MAC: Least significant bit of first byte = 0
- 65 hex = 01100101 binary → LSB = 1 (actually multicast)
- Correction: All options except A are unicast MAC addresses
- FF-FF-FF-FF-FF-FF is broadcast address
📚 SECTION B: (60 MARKS)
Attempt THREE (3) out of FOUR (4) questions.
** Question Six**
a. What do you understand by UDP?
(2 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
UDP (User Datagram Protocol):
- Connectionless transport layer protocol
- Provides minimal, best-effort delivery service
- No guarantees for delivery, ordering, or duplicate protection
- Low overhead with 8-byte header
- Suitable for real-time applications like VoIP, streaming
b. Briefly explain when it is appropriate for application designers/developers to use UDP instead of TCP.
(4 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
When to use UDP instead of TCP:
- Real-time applications: VoIP, video conferencing, live streaming
- Simple query-response: DNS lookups, DHCP requests
- Multicast/broadcast: Applications sending to multiple recipients
- Low latency requirements: Gaming, financial trading
- Custom reliability: When application needs specific reliability mechanisms
- Minimal overhead: When header overhead must be minimized
c. Suppose you are given the following dump of a TCP header in Hexadecimal format as D31C 0050 0001 0001 0002 0000 5002 07FE 0000 0000; analyze the following details:
i. What is the destination port number?
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
Destination Port: 80
- Bytes 2-3: 0050 hexadecimal
- 0050 hex = 80 decimal
ii. What is the source port number?
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
Source Port: 54044
- Bytes 0-1: D31C hexadecimal
- D31C hex = 54044 decimal
iii. What is the acknowledgement number?
(2 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Acknowledgement Number: 65538
- Bytes 8-11: 0001 0001 hexadecimal
- Combined: 0x00010001 = 65537 decimal
- Correction: Should be 65537 (not 65538)
iv. What is the sequence number?
(2 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Sequence Number: 65536
- Bytes 4-7: 0001 0000 hexadecimal
- Combined: 0x00010000 = 65536 decimal
v. What is the window size?
(2 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Window Size: 2046
- Bytes 14-15: 07FE hexadecimal
- 07FE hex = 2046 decimal
vi. Based on part i. and ii., is the segment from client to server or vice versa?
(2 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
From Client to Server
- Destination port 80 is well-known HTTP server port
- Source port 54044 is ephemeral client port
- Therefore, segment is from client to web server
vii. Based on part i., name the intended application layer service as well as its associated protocol.
(4 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Application Layer Service: HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol)
- Destination port 80 indicates HTTP service
- Protocol: TCP (since this is a TCP header analysis)
- Used for web browsing and web services
- Stateless request-response protocol
Question Seven
a. Consider a situation where Host W sends two TCP segments back to back to Host Z. The first segment has sequence number 4125; the second has sequence number 4165:
i. What is the window size?
(3 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Cannot determine window size from given information
- Window size is advertised by receiver, not determined by sequence numbers
- Sequence numbers indicate data bytes sent, not window capacity
- Need receiver’s advertised window to determine window size
ii. Suppose the first segment is lost but the second segment arrives at Z. In the acknowledgement that host Z sends to Host W, what will be the acknowledgement number?
(4 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Acknowledgement Number: 4125
- TCP uses cumulative acknowledgements
- Missing segment with SEQ 4125 means receiver expects byte 4125 next
- ACK number indicates next expected byte
- Even though segment with SEQ 4165 arrived, it cannot be acknowledged due to gap
iii. Assuming the first segment is retransmitted and the second segment is eventually acknowledged, what will be the sequence number of the third segment?
(4 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Sequence Number of Third Segment: 4205
- First segment: SEQ 4125, length = 4165 - 4125 = 40 bytes
- Second segment: SEQ 4165, length unknown but assume same 40 bytes
- Total sent = 80 bytes
- Third segment SEQ = 4125 + 80 = 4205
b. Explain three ways through which TCP attains reliable delivery of data.
(9 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
TCP Reliability Mechanisms:
- Sequence Numbers and Acknowledgements
- Each byte assigned unique sequence number
- Receiver sends ACK for received data
- Enables detection of missing or out-of-order segments
- Retransmission Timeout (RTO)
- Timer set for each transmitted segment
- If ACK not received before timeout, segment retransmitted
- Adaptive timeout based on round-trip time measurements
- Selective Acknowledgements (SACK)
- Receiver can acknowledge non-contiguous data blocks
- Allows retransmission of only missing segments
- More efficient than cumulative acknowledgements alone
- Checksums
- Each segment includes checksum for error detection
- Corrupted segments are discarded and retransmitted
- Ensures data integrity during transmission
- Flow Control
- Prevents receiver overflow using window size advertisement
- Maintains reliable delivery by matching sender rate to receiver capacity
Question Eight
a. State at least two reasons as to why you would use a Web Proxy Server in your organization.
(4 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Web Proxy Server Benefits:
- Content Caching: Stores frequently accessed web content, reducing bandwidth usage and improving response times
- Security: Filters malicious content, blocks access to inappropriate websites, provides anonymity
- Access Control: Enforces organizational policies, restricts access to specific sites or content types
- Monitoring and Logging: Tracks user web activities for security and compliance purposes
b. Study Figure 1 closely and explain why computer A cannot communicate with computer B.
(6 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Communication Issues:
- Incorrect Subnet Mask on Computer A: 255.256.255.240 is invalid (256 is not valid octet value)
- Incorrect Subnet Mask on Computer B: 255.256.255.245 is invalid
- Network Mismatch:
- Computer A: 192.168.10.30/28 (assuming valid mask 255.255.255.240)
- Computer B: 192.168.20.0/29 (assuming valid mask 255.255.255.248)
- Different subnets require router configuration
- Default Gateway Issues: Gateways may not be properly configured or reachable
- Router Configuration: Router interfaces may not be properly configured for inter-VLAN routing
c. What are four basic configurations that a DHCP server deploys to the client machine?
(4 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
DHCP Configuration Parameters:
- IP Address: Dynamic assignment of unique IP address
- Subnet Mask: Defines network and host portions of IP address
- Default Gateway: Router interface for external communication
- DNS Servers: Domain Name System servers for name resolution
- Lease Time: Duration for which IP assignment is valid
d. Results of ipconfig command on a Windows machine indicated IP configuration shown in Figure 2, explain this configuration in relation to the DHCP server.
(6 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
APIPA Configuration Explanation:
- 169.254.103.72: APIPA (Automatic Private IP Addressing) address
- Cause: DHCP server unreachable or failed during IP assignment
- Subnet Mask 255.255.0.0: Default for APIPA range 169.254.0.0/16
- No Default Gateway: APIPA doesn’t provide gateway, limiting to local network
- Implication: Computer can only communicate with other APIPA devices on same segment
- Resolution: Check DHCP server availability, network connectivity, or DHCP service status
Question Nine
a. Discuss the impact of Classless Inter-Domain Routing with respect to:
i. Size of routing tables
(3 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Routing Table Size Impact:
- Reduction: CIDR allows route aggregation/summarization
- Multiple classful networks can be represented by single CIDR block
- Example: 192.168.0.0/16 instead of 256 separate Class C networks
- Slows the growth of Internet routing tables
ii. Routing efficiency
(3 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Routing Efficiency Impact:
- Improvement: More specific routes available when needed
- Hierarchical routing reduces table lookups
- Better path selection with variable-length prefixes
- Reduced routing update traffic due to aggregation
iii. Memory requirements of core routers
(3 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Memory Requirements Impact:
- Reduction: Fewer routing table entries require less memory
- More efficient use of router memory resources
- Enables routers to handle larger networks with same memory
- Delays hardware upgrade requirements
iv. CPU cycles of core routers
(3 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
CPU Cycles Impact:
- Reduction: Fewer entries mean faster routing table lookups
- Reduced processing for routing updates
- More efficient longest prefix match algorithms
- Better overall router performance
v. Price of core routers
(3 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Router Price Impact:
- Cost Savings: Less powerful routers can handle larger networks
- Extended lifespan of existing router hardware
- Reduced need for frequent hardware upgrades
- More cost-effective network scaling
b. Given networks and their corresponding subnet masks as follows:
- 172.1.4.0/25
- 172.1.4.128/25
- 172.1.5.0/24
- 172.1.6.0/24
- 172.1.7.0/24
What is the:
i. Aggregate route
(3 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Aggregate Route: 172.1.4.0/22
- Networks: 172.1.4.0-172.1.7.255
- Common prefix: 172.1.4.0 with 22-bit mask
- Covers entire range from 172.1.4.0 to 172.1.7.255
ii. Subnet Mask of the aggregate route
(2 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Subnet Mask: 255.255.252.0
- /22 mask in dotted decimal notation
- 255.255.252.0 provides 1024 addresses (172.1.4.0 - 172.1.7.255)
c. Suppose router W has built up the routing table shown in Table 1. The router can deliver packets directly over interfaces 0 and 1, or it can forward packets to routers R2, or R3. Describe what the router does with a packet addressed to each of the following destinations:
i. 192.4.153.90
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
Forward to Interface 0
- Matches 192.4.153.0/26 route
- Next hop: Interface 0 (direct delivery)
ii. 28.96.39.14
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
Use Default Route to R2
- No specific match in routing table
- Use default route 0.0.0.0/0 via R2
iii. 128.96.50.12
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
Use Default Route to R2
- No specific match for 128.96.50.12
- Use default route via R2
iv. 128.96.50.151
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
Use Default Route to R2
- No specific match for 128.96.50.151
- Use default route via R2
v. 192.4.53.17
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
Use Default Route to R2
- No specific match for 192.4.53.17
- Use default route via R2
END OF EXAMINATION PAPER
Study Tips
- Practice TCP header analysis and sequence number calculations
- Understand CIDR and route aggregation concepts
- Master DHCP configuration and troubleshooting
- Review routing table interpretation
- Practice subnetting and VLSM calculations