Object Oriented Programming Exam - CP 215
THE UNIVERSITY OF DODOMA
COLLEGE OF INFORMATICS AND VIRTUAL EDUCATION
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING
UNDERGRADUATE UNIVERSITY EXAMINATIONS
FIRST SEMESTER 2019/2020
CS 213: OBJECT ORIENTED PROGRAMMING IN JAVA
Date: 19th February, 2020
Time Allocated: 3 Hours
Start: 11:45 AM
Instructions:
- This examination consists of six (6) questions;
- Answer all questions from section A and two questions from section B;
- All University of Dodoma Examination Regulations Apply.
SECTION A (40 MARKS)
Question One
Provide short answers to each of the following questions:
(2.5 Marks Each)
a) Why method main is declared static?
b) What is the name of a mechanism used to destroy object references that are no longer in use?
c) Differentiate between method overriding and method overloading?
d) What is a checked exception? Give an example of this type of exception.
e) int i = 5 / 2; compute the equation
f) double c = (4 * 3) / 7; compute the equation
g) What is the use of the so called “White space” in Java programming?
h) Outline three ways used for providing comments in Java programs.
i) Mention a method that is implicitly called by JAVA when you execute a Java application.
j) Why is it possible to use some of the classes from Java API such as System and String without explicitly importing them?
Question Two
a) Write a method header for each of the following methods. (2 Marks Each)
i. Method basket, which contains a String parameter called cup, and does not return any value.
ii. Method dodoma, which takes a double-precision floating-point argument radius and returns a double-precision floating-point result.
iii. Method smallest, which does not take any arguments but it returns an integer.
iv. Method instructions, which does not take any arguments and does not return a value.
v. Method intToFloat, which takes integer argument number and returns a float.
Question Three
a) Identify and describe the error in the following program.
(2 Marks)
public final class Animal { }
public final class Lion extends Animal { }b) What is the output of the following expressions?
(3 Marks)
new String("i am an intellectual").substring(0, 2).toUpperCase() + " am an " +
new String("i am an intellectual").substring(6, 9).toUpperCase() + " intellectual"c) Write a method called reverse(), which takes an array of integers and reverses its contents. For example, the reverse of {1,2,3,4} is {4,3,2,1}.
(5 Marks)
d) What is the source of error in this piece of code?
(5 Marks)
class CalculationOne{
void sum(int x, int y){System.out.println(x + y);}
}
class CalculationTwo extends CalculationOne {
int sum(int x, int y){return(x + y);}
public static void main(String args[]) {
CalculationTwo object = new CalculationTwo();
object.sum(20, 20);
}
}SECTION B (60 MARKS)
Question Four
a) Consider the classes Student and Address. Every student has an address, therefore the relationship between student and address is a Has-A relationship. But if you consider it in the reverse, it would not make any sense as it is not necessary for the Address to contain a Student. Write three java Classes to implement this relationship. Note that Address may contain street number, city and country while student class may have address, student name and student id. (15 Marks)
b) Encapsulation is all about wrapping variables and methods in one single unit. Also, it is known as data hiding. Thus, when you design your class you may (and you should) make your variables hidden from other classes and provide methods to manipulate the data instead. Now consider the Car class which has two fields-name and topSpeed. The getter and setter methods: getName, setName, setTopSpeed etc. are declared in this class. Those methods are exposed to “outsiders” and can be used to change and retrieve data from the Car object. Write two java classes to demonstrate this concept of encapsulation. (15 Marks)
Question Five
a) Write a java program using swing GUI components to create a Frame which contains two text fields labelled Name and Age for capturing user name and age respectively, four buttons named Submit, View, Clear and Exit. When user enters name and age on the text fields and clicks submit button, the name and age should be submitted to MySQL database named user_database, in the table called user_table. When user clicks view button, the name and age should be retrieved from the database and displayed on the dialog window. When user clicks clear button, the text fields have to be cleared if they contain any data value. When user clicks exit button, the program should close. In case of database connection failure, program should handle the thrown Exception using try-catch block with the message “database connection failed” displayed on the dialog window. All used resources should finally be closed inside try-finally block. (15 Marks)
b) Write java application using Swing components that will allow Mr. Siphael to record test score for 800 students taking CS 213. The application should accept inputs through dialog window and return the results in two separate dialog windows. The first window should output class average score and the second window should output the test scores entered in ascending order. Organize your program in one method called testScore () and use method main () to test the application. Do not create any object to access the testScore () method. (15 Marks)
Question Six
You are required to write an application that can determine payments for employees and invoices alike, by first creating interface Payable, which contains method getPaymentAmount that returns a double amount that must be paid for an object of any class that implements the interface. Method getPaymentAmount is a general-purpose method to be implemented by classes that implements interface Payable. After declaring interface Payable, we introduce class Invoice, which implements interface Payable. We then introduce class Employee such that it also implements interface Payable. Classes Invoice and Employee both represent things for which the company must be able to calculate a payment amount. Both classes implement the Payable interface, so a program can invoke method getPaymentAmount on Invoice objects and Employee objects alike. This enables the polymorphic processing of Invoices and Employees required for the company’s accounts payable application. Class Invoice represents a simple invoice that contains billing information for only one kind of part. The class declares private instance variables partNumber, partDescription, quantity and pricePerItem. Class Invoice also contains a constructor, get methods and a toString method that returns a String representation of an Invoice object. Class Employee should implement Payable interface. It contains employee’s firstName, lastName, and employeeID. It also contains a constructor for initialization of instance variable a toString method for returning its string representation. Salaried employee is paid a fixed weekly salary regardless of the number of hours worked. Therefore SalariedEmployee class should contain a unique variable called salary, a constructor, a toString method for returning its string representation. Figure 1 shows a schematic representation between Payable interface, Invoice, Employee and SalariedEmployee classes. (30 Marks)
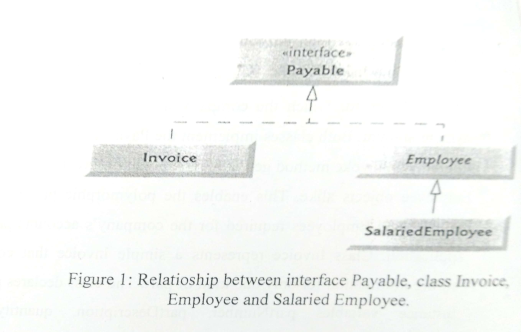 Figure 1
Figure 1