Object Oriented Programming Exam - CP 215
University of Dodoma
College of Informatics and Virtual Education
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
End of Semester University Examination for the 2023/2024 Academic Year
Course Name: Object Oriented Programming
Paper Code Number: CP 215
Date of Examination: [Date]
Time: [Time]
Duration: 3 Hours
SECTION A: (40 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section.
Question One
Read each question carefully and choose the most correct response.
(1 Mark Each)
i. Which statement is not true about constructor?
A. There is no return statement in the body of constructor
B. There is no return type given in constructor signature
C. Constructor cannot be overloaded
D. It may include this and super keywords in its body
E. The name of the constructor is the same as the name of class
ii. The Java compiler translates source code into:
A. Machine code.
B. Assembly code.
C. Object code
D. Byte code.
E. JVM code.
iii. Which of the following characteristics of an object-oriented programming language restricts behaviour so that an object can only perform actions that are defined for its class?
A. Encapsulation
B. Inheritance
C. Dynamic Binding
D. Polymorphism
E. Abstraction
iv. Translate the statement “If the value of temperature is between 20.0 and 40.0, print ‘very cold’” into Java.
A. if(!temperature < 20.0 || temperature > 40.0)) System.out.println("very cold");
B. if(20.0 <= temperature <= 40.0) System.out.println("very cold");
C. if(temperature >= 20.0 || temperature <= 40.0) System.out.println("very cold");
D. if(temperature >= 20.0 || temperature <= 40.0) System.out.println("very cold");
E. if(!temperature < 20.0 && temperature > 40.0)) System.out.println("very cold");
v. Which of the following statement describes dynamic resizing as it applies to the ArrayList class?
A. The size of a new ArrayList object must be specified at instantiation.
B. The size of an ArrayList object can be iterated throughout a program.
C. The size of an ArrayList object is fixed at instantiation.
D. The object changes size dynamically as new elements are added.
E. Both A and B
vi. Which of the following is TRUE?
A. The multiple catch blocks should be listed in the order from general exception classes to more specialized ones.
B. If there is no exception, the finally block will not be executed.
C. If there are multiple catch blocks, only the first one matching the exception will be executed.
D. If there are multiple catch blocks, all blocks that match the exception will be executed.
E. If no exception is thrown, the first catch block will be executed.
vii. The static variable declared in a class is called:
A. Global variables
B. Local Variables
C. Class variables
D. Instance variables
E. Object variables
Carefully read the following program and use it to answer questions that follow. Comments indicate where missing components of the program are to be placed.
public class MyMain {
public static void main(String [] args) {
// (2) print the greeting
// (3) construct a MyClass object called myObject
// (4) update() {
}
}
class MyClass {
// (1) definition of MyClass constructor
public static void greetings() {
// definition of greets
}
public void update(int num, String title) {
// definition of update
}
public void print() {
// definition of print
}
private int numOfItems;
private String reportTitle;
}viii. Suppose you wish to construct MyClass object called myObject at line (3) above. Which of the following statement will correctly do this?
A. MyClass myObject;
B. MyClass myObject = MyClass();
C. MyClass myObject = new(MyClass);
D. MyClass myObject = new MyClass();
E. myObject.MyClass();
ix. Suppose you wish to call the method that prints the greeting, at line (2) above. Which of the following statement(s) will call this method correctly?
A. myObject.greetings();
B. greetings();
C. MyClass.greetings();
D. Both A and B
E. Both B and C
x. Suppose you wish to call the update method at line (4) above. Which of the following statements will call this method correctly?
A. myObject.update(4, "CP 215");
B. update(myObject(4, "CP 215"));
C. update(4, "CP 215");
D. MyClass.myObject.update(4, "CP 215");
E. MyClass.update(4, "CP 215");
Question Two
Match the item in Column A with its corresponding item in Column B.
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| i. Used to call a method in superclass. | A. int, double, Float |
| ii. Identify and discard objects that are no longer needed by a program. | B. abstract |
| iii. Statement objects return SQL query results. | C. Encapsulation |
| iv. Examples of wrapper classes | D. final class |
| v. It is always invoked when a new object is created. | E. Inheritance |
| vi. The base class of unchecked exception. | F. Collection of abstract class |
| vii. Prevent anyone from instantiating the class directly. | G. Class |
| viii. Cannot be extended. | H. Double, Integer, Character |
| ix. Used to submit a query to database. | I. Object |
| x. Private members, getter and setter methods. | J. Garbage collection |
| K. Statement | |
| L. Composition | |
| M. ResultSet | |
| N. Overriding | |
| O. Enhanced for loop | |
| P. ArrayList class | |
| Q. super | |
| R. Specialization | |
| S. Instance of class | |
| T. RuntimeException | |
| U. Late binding | |
| V. Polymorphism | |
| W. Collection of abstract methods | |
| X. Overloading | |
| Y. Constructor | |
| Z. Interface |
Question Three
Write True for the correct statement and False for the incorrect statement in your answer booklet.
a. Java supports multiple inheritance for class but only single inheritance for interface.
b. A try block can occur without an accompanying catch clause or finally block.
c. If class C implements interface IFace but fails to define all of the methods defined in IFace, then C is abstract class.
d. If a subclass sub overrides method m inherited from superclass super, then m must have the same signature in sub and super.
e. The code segment int x = 8; System.out.println(x++) prints 8 to the standard output.
f. If a class C does not define any constructors, then C has a private accessible no-argument constructor.
g. Every exception thrower must be either an exception catcher or an exception propagator.
h. In class inheritance, a subclass inherits only the non-private members of the superclass.
i. Given a string declaration String s = new String ("Have a nice Day") the methods s.charAt(1) and s.length() will return H and 15 respectively.
j. When an object is passed to a method, a copy of each of the object’s data members are created and passed to the method.
Question Four
a. For each of the following methods, write the method header.
(1.5 Marks Each)
i. Method intToFloat, which takes integer argument number and returns a float.
ii. Method hypotenuse, which takes two double-precision, floating-point arguments side1 and side2 and returns a double-precision, floating-point result.
b. Carefully read the instructions given, and for each instruction, write a code segment to accomplish the stated task.
i. Declare and instantiate a two-dimensional array called intArr that holds int values and has 8 columns and 5 rows.
(1.5 Marks)
ii. Fill each cell of the intArr array in b(i) with the result of multiplying that cell’s column index by its row index. Do not hardcode the length of the array in any way.
(2.5 Marks)
iii. Print each row of the intArr array in order on separate lines. Each entry should be separated by single space. The last entry in each row should be followed by a colon (:) and then the sum of the entries in the row.
(3 Marks)
SECTION B: (60 MARKS)
Attempt any THREE (3) out of FOUR (4) questions provided.
Question Five
a. Consider the following code: What will be printed when m(0) and m(-2) are executed sequentially?
(5 Marks)
public class A {
public static double m(int x) {
int y = x;
try {
System.out.println("one");
y = 5/x;
System.out.println("two");
return 5/(x+2);
} catch (RuntimeException e) {
System.out.println("three");
y = 5/(x+1);
System.out.println("four");
}
System.out.println("five");
y = 4/x;
System.out.println("six");
return 1/x;
}
}b. What will be printed when the following code is executed?
(5 Marks)
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class CP215 {
public static void main(String args[]) {
ArrayList numbers = new ArrayList();
for (int k = 1; k <= 10; k++)
numbers.add(new Integer(k));
int sum = 0;
for (k = 0; k < numbers.size(); k++) {
Integer temp = (Integer) numbers.get(k);
sum += temp.intValue();
}
double average = (double) sum / numbers.size();
System.out.println(average);
}
}c. Will the following program compile and run successfully? If yes, write the output; otherwise, briefly explain and write code segment needed to be corrected.
(5 Marks)
class myClass {
void myMethod() throws IOException {
System.out.println("CP 215");
}
}
class myclass2 extends myClass {
void myMethod() throws Exception {
System.out.println("In Child class");
}
}
public class ClassTest {
public static void main(String args[]) {
myClass S = new myClass2();
S.myMethod();
}
}d. What will be printed when the following code is executed?
(5 Marks)
public class Test {
private static final value = 5;
public static void main(String []args) {
int total, value = 4;
total = value + value;
total = total + someMethod(total);
System.out.println(total);
}
public static int someMethod(int val) {
return value;
}
}Question Six
Figure 1 shows a schematic representation of Payable interface, Invoice, Employee and SalariedEmployee classes.
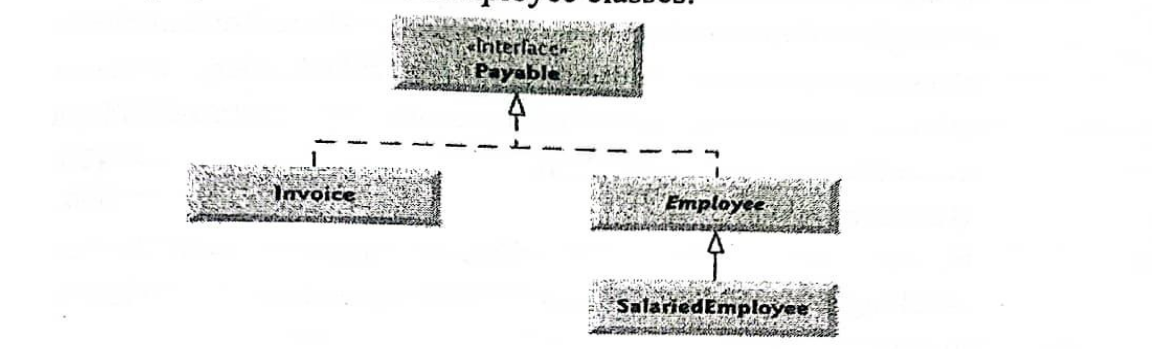
(Figure 1: Relationship between interface Payable, class Invoice, Employee and SalariedEmployee.)
Use the following information to write an application to determine payments for employees and invoices. You are required to create interface Payable, which contains method getPaymentAmount that returns a double amount that must be paid for an object of any class that implements the interface. Method getPaymentAmount is a general-purpose method to be implemented by classes that implements interface Payable. After declaring Payable interface, define class Invoice and Employee, such that they implement interface Payable. Classes Invoice and Employee both represent things for which the company must be able to calculate a payment amount. Both classes implement the interface Payable, so that a program can invoke method getPaymentAmount on Invoice objects and Employee objects. Class Invoice represents a simple invoice that contains billing information for only one kind of part. The class declares private instance variables partNumber, partDescription, quantity and pricePerItem. Class Invoice also contains a constructor, get methods and a toString method that returns a String representation of an Invoice object. The class Employee contains employee’s firstName, lastName, and employeeID. It also contains a constructor for initialization of instance variable and a toString method for returning its string representation. Salaried employee is paid a fixed weekly salary regardless of the number of hours worked. Therefore, SalariedEmployee class should contain a unique variable called salary, a constructor, a toString method for returning its string representation. Include main method to test your application.
(20 Marks)
Summary Of the Question Use the following information to write an application to determine payments for employees and invoices. You are required to:
- Create interface
Payable, which contains methodgetPaymentAmountthat returns a double amount that must be paid for an object of any class that implements the interface. - Define class
InvoiceandEmployeesuch that they implement interfacePayable. - Class
Invoicerepresents a simple invoice that contains billing information for only one kind of part. The class declares private instance variablespartNumber,partDescription,quantity, andpricePerItem. Include a constructor, get methods, and atoStringmethod. - Class
Employeecontains employee’sfirstName,lastName, andemployeeID. Include a constructor and atoStringmethod. - Class
SalariedEmployee(a subclass ofEmployee) should contain a unique variable calledsalary, a constructor, and atoStringmethod. - Include a
mainmethod to test your application.
(20 Marks)
Question Seven
Figure 2 shows a bank that offers its customers with the saving and checking account types: carefully read the information given and use it to answer the questions that follow:
Figure 2: Bank Account Classes
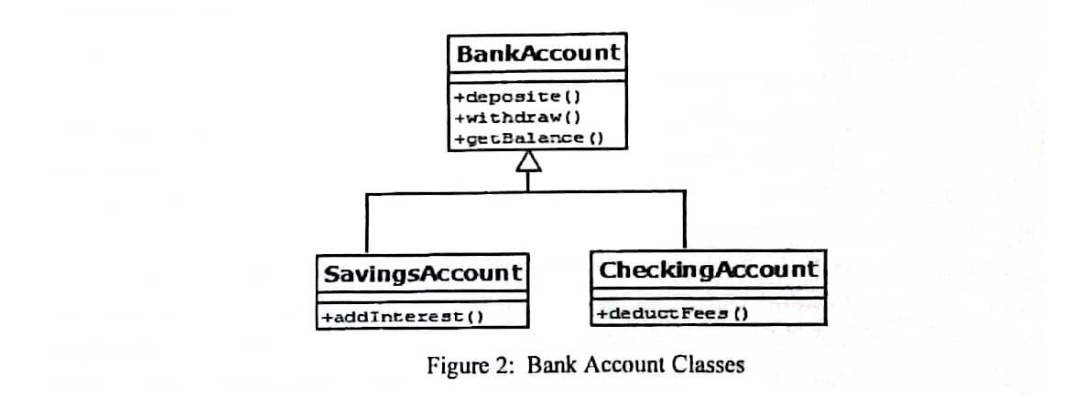
The checking account has no interest; it gives customer a maximum six number of free transactions per month, and charges a transaction fee of Tsh 2000 for each additional transaction. The savings account earns interest that calculated monthly. The interest is calculated as 1.5 percent of the balance for the last day of the month. All bank accounts support the getBalance method, which reports the current balance. They also support the deposit and withdraw methods, although the details of the implementation differ. For, a checking account must keep track of the number of transactions to account for the transaction fees. The checking account needs a method deductFees to deduct the monthly fees and to reset the transaction counter. The deposit and withdraw methods must be overridden to count the transactions. The method withdraw should ensure that the withdrawal amount does not exceed the account’s balance. If it does, the balance should be left unchanged and the method should throw exception indicating that “Withdrawal amount exceeds the account balance”. The savings account needs a method addInterest to add interest.
a. Write program that implements the given information. (12 Marks)
b. Write class AccountTester with main method for the implementation in a) that reads in the initial values from the keyboard, create object references and call other methods. When the method withdraw is called use try-catch block to catch the exception thrown from this method. (Note observe the rules for method overriding with Exception Handling). (8 Marks)
Question Eight
a. Assume that you have a MySQL database named EmployeeDB running on localhost server and it has a table called EmployeeInfo with four columns: p_id, first_name, last_name and phone_number. Write a Java program that will establish JDBC connection to the database and query the database’s EmployeeInfo table to display first name, last name and phone number of the employees. Also, provide try-catch-finally block for exception handling where appropriate. Given the driver class is com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, the port number is 3306. Use root for both username and password.
(10 Marks)
b. Create a Java class Book representing a book with the following attributes: title, author, and price. Also, create a class Library that contains an array of Book objects. Implement a method totalPrice() in the Library class that calculates and returns the total price of all the books in the library. Assume that each book has a unique title. Write a test program to demonstrate the functionality of the Library class.
(10 Marks)
Summary Of Question Eight
a. Assume you have a MySQL database named EmployeeDB running on localhost server with a table EmployeeInfo with columns: p_id, first_name, last_name, phone_number.
Write a Java program that:
- Establishes JDBC connection to the database.
- Queries the
EmployeeInfotable to display first name, last name, and phone number. - Uses try-catch-finally for exception handling.
Driver:com.mysql.jdbc.Driver, Port:3306, Username:root, Password:root.
(10 Marks)
b. Create a Java class Book with attributes: title, author, price.
Create a class Library that contains an array of Book objects.
Implement a method totalPrice() in Library that returns the total price of all books.
Assume each book has a unique title.
Write a test program to demonstrate the functionality.
(10 Marks)
END OF EXAMINATION PAPER