Computer Networking Protocols - Exam
THE UNIVERSITY OF DODOMA
OFFICE OF THE DEPUTY VICE CHANCELLOR ACADEMIC, RESEARCH AND CONSULTANCY
COLLEGE OF INFORMATICS AND VIRTUAL EDUCATION
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
End of Semester One University Examination for the 2023/2024 Academic Year
Course Name: Computer Networking Protocols
Paper Code Number: CN 211
Date of Examination: 6th March, 2024
Time: 11:45-14:45
Duration: 3 Hours
Venue(s): FL2, LRB 105, 106, 004C, 004D, 101&102
Sitting Programme(s): BSc. CSDFE2, HIS2, CNISE2, DCBE2, TE2, CE2, SE2, BIS2, SE3, CS2, CS3, CNISE3, TE3&CE3
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
i. This examination paper consists of TWO (2) sections with EIGHT (8) questions in THIRTEEN (13) printed pages.
ii. The total score for this examination is 100 points. Marks are allocated at the end of each question.
iii. Answer all questions in Section A and THREE (3) questions in Section B.
iv. ALL responses should be written in the answer book provided.
v. Insert the examination paper into the answer book after the examination. Students should not take any examination paper(s) out of the examination room.
vi. All regulations guiding the administration of university examinations apply.
SECTION A: (40 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section.
Question One - Multiple Choice
(0.5 Mark Each)
1. What is the correct number of usable subnetworks and hosts for the IP network address 192.168.35.0 submitted with a /28 mask?
- A. 12 networks /11 hosts
- B. 12 networks /12 hosts
- C. 12 networks /14 host
- D. 14 networks /14 hosts
- E. 13 networks /13 hosts
Answer (Click to show)
D. 14 networks /14 hosts
- /28 mask = 255.255.255.240
- Subnet bits: 4 (2^4 = 16 total subnets, 14 usable)
- Host bits: 4 (2^4 - 2 = 14 usable hosts)
2. Which OSI layer header contains the address of a destination host that is on another network?
- A. Application
- B. Session
- C. Transport
- D. Network
- E. Data link
Answer (Click to show)
D. Network
- Network layer (Layer 3) handles logical addressing and routing between different networks
- Contains IP addresses for source and destination hosts
3. Refer to the Figure 1. If host A sends an IP packet to host B, what will the destination address be in the frame when it leaves host A?
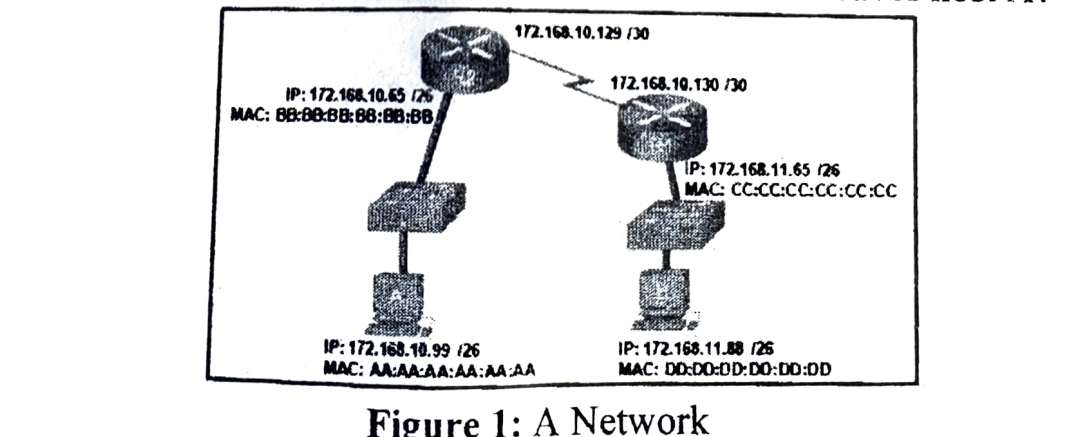
- A. DD:DD:DD:DD:DD
- B. 172.168.10.99
- C. 172.168.10.65
- D. AA:AA:AA:AA:AA:AA
- E. BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
Answer (Click to show)
E. BB:BB:BB:BB:BB
- Hosts A and B are on different networks
- Frame destination MAC will be the router’s interface (default gateway)
- Router’s MAC BB:BB:BB:BB:BB receives the frame for forwarding
4. A network administrator is adding a new LAN to a branch office. The new LAN must support 25 connected devices. What is the smallest network mask that the network administrator can use for the new network?
- A. 255.255.255.228
- B. 255.255.255.192
- C. 255.255.255.224
- D. 255.255.255.240
- E. 255.255.255.128
Answer (Click to show)
C. 255.255.255.224
- Need 25 hosts → 2^n - 2 ≥ 25 → n = 5 host bits (30 usable hosts)
- Subnet mask: /27 = 255.255.255.224
- 32 - 5 host bits = 27 network bits
5. Which frame field is created by a source node and used by a destination node to ensure that a transmitted data signal has not been altered by interference, distortion, or signal loss?
- A. Frame check sequence field
- B. Error correction process field
- C. Flow control field
- D. Time to Live field
- E. User Datagram Protocol field
Answer (Click to show)
A. Frame check sequence field
- FCS uses CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check) for error detection
- Source calculates CRC, destination verifies it
- Detects errors caused by interference or signal issues
6. An administrator is trying to configure the switch but receives the error message. What is the problem?
Switch1> config t
Invalid input detected at '^' marker.
- A. The entire command, configure terminal, must be used.
- B. The administrator must connect via the console port to access global configuration mode.
- C. The administrator is already in global configuration mode.
- D. The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.
- E. Nothing is wrong.
Answer (Click to show)
D. The administrator must first enter privileged EXEC mode before issuing the command.
Switch1>indicates user EXEC mode- Need
enablecommand to enter privileged EXEC modeSwitch1#- Then
configure terminalcan be used
7. What will happen if the default gateway address is incorrectly configured on a host?
- A. The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- B. The host cannot communicate with other hosts in the local network.
- C. A ping from the host to 127.0.0.1 would not be successful.
- D. The switch will not forward packets initiated by the host.
- E. The host can communicate with other hosts
Answer (Click to show)
A. The host cannot communicate with hosts in other networks.
- Default gateway is the router interface on the local network
- Essential for routing packets to other networks
- Local communication (same subnet) still works via ARP
8. Which scenario describes a function provided by the transport layer?
- A. A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- B. A student is using a classroom VoIP phone to call home. The unique identifier burned into the phone is a transport layer address used to contact another network device on the same network.
- C. A corporate worker is accessing a web server located on a corporate network. The transport layer formats the screen so the web page appears properly no matter what device is being used to view the web site.
- D. A student is playing a short web-based movie with sound. The movie and sound are encoded within the transport layer header.
- E. All of the above
Answer (Click to show)
A. A student has two web browser windows open in order to access two web sites. The transport layer ensures the correct web page is delivered to the correct browser window.
- Transport layer uses port numbers for process-to-process delivery
- Ensures data reaches correct application (browser window)
- Multiplexing/demultiplexing function
9. Which two protocols operate at the top layer of the TCP/IP protocol suite?
- A. POP and IP
- B. DNS and DHCP
- C. POP and DNS
- D. IP and TCP
- E. POP, IP and TCP
Answer (Click to show)
C. POP and DNS
- TCP/IP Application layer protocols: POP3, DNS, DHCP, HTTP, SMTP, etc.
- IP (Internet) and TCP (Transport) are lower layer protocols
10. Which layers of the OSI model map to the application layer of the TCP/IP model?
- A. Transport, Network and Application.
- B. Application, Session and Data link.
- C. Application, Session and Presentation.
- D. Application, Session and Transport.
- E. Transport, Network and Presentation and Session.
Answer (Click to show)
C. Application, Session and Presentation.
- TCP/IP Application layer = OSI Application + Presentation + Session layers
- TCP/IP combines upper OSI layers into single Application layer
11. Which two statements are correct in a comparison of IPv4 and IPv6 packet headers?
- A. The Destination Address field is new in IPv6.
- B. The Time-to-Live field from IPv4 has been replaced by the Hop Limit field in IPv6.
- C. The Source Address field name from IPv4 is kept in IPv6.
- D. The Version field from IPv4 is not kept in IPv6.
- E. All of the above
Answer (Click to show)
B. The Time-to-Live field from IPv4 has been replaced by the Hop Limit field in IPv6.
- IPv4 TTL becomes IPv6 Hop Limit
- Both serve same purpose: prevent infinite packet looping
12. A client packet is received by a server. The packet has a destination port number of 67. What service is the client requesting?
- A. Telnet
- B. FTP
- C. SSH
- D. DHCP
- E. FTP and SSH
Answer (Click to show)
D. DHCP
- Port 67 = DHCP server port
- Used for dynamic IP address assignment
13. What is an advantage to using a protocol that is defined by an open standard?
- A. An open standard protocol is not controlled or regulated by standards organizations.
- B. A company can monopolize the market.
- C. It encourages competition and promotes choices.
- D. The protocol can only be run on equipment from a specific vendor
- E. All of the above
Answer (Click to show)
C. It encourages competition and promotes choices.
- Open standards enable interoperability between different vendors
- Prevent vendor lock-in and promote innovation
14. Which information does the show startup-config command display?
- A. The IOS image copied into RAM
- B. The bootstrap program in the ROM
- C. The contents of the saved configuration file in the NVRAM
- D. The contents of the current running configuration file in the RAM
- E. Just the bootstrap program
Answer (Click to show)
C. The contents of the saved configuration file in the NVRAM
- startup-config = saved configuration in NVRAM
- running-config = current configuration in RAM
15. Which one of the following fields is present in both TCP header and UDP header?
- A. Acknowledgement number
- B. Urgent pointer
- C. Sequence number
- D. Checksum
- E. None of these
Answer (Click to show)
D. Checksum
- Both TCP and UDP headers include checksum fields for error detection
- Other fields are TCP-specific
16. Which of the following is incorrect about User Datagram Protocol?
- A. UDP is unreliable Transport Protocol
- B. There is no window mechanism in UDP
- C. There is a robust error control mechanism in UDP
- D. The user may overflow with incoming messages
- E. All of the above
Answer (Click to show)
C. There is a robust error control mechanism in UDP
- UDP has minimal error control (only checksum)
- No retransmission, sequencing, or flow control
17. Which value that is contained in an IPv4 header field is decremented by each router that receives a packet?
- A. Differentiated Services
- B. Time-to-Live
- C. Fragment Offset
- D. Header Length
- E. Checksum
Answer (Click to show)
B. Time-to-Live
- TTL prevents infinite packet looping
- Decremented by each router, packet discarded when TTL=0
18. What is the purpose of the TCP sliding window?
- A. To ensure that segments arrive in order at the destination
- B. To request that a source decrease the rate at which it transmits data
- C. To inform a source to retransmit data from a specific point forward
- D. To end communication when data transmission is complete
- E. None of the above
Answer (Click to show)
B. To request that a source decrease the rate at which it transmits data
- Sliding window implements flow control
- Prevents sender from overwhelming receiver
19. What are the three parts of an IPv6 global unicast address?
- A. subnet ID, global routing prefix and interface ID
- B. global routing prefix, interface ID and subnet mask
- C. interface ID, broadcast address and subnet mask
- D. subnet ID, interface ID and subnet mask
- E. subnet mask, interface ID.
Answer (Click to show)
A. subnet ID, global routing prefix and interface ID
- Global routing prefix: network portion (typically 48 bits)
- Subnet ID: subnet within organization (16 bits)
- Interface ID: host identifier (64 bits)
20. What is one main characteristic of the data link layer?
- A. It generates the electrical or optical signals that represent the 1 and 0 on the media.
- B. It converts a stream of data bits into a predefined code.
- C. It shields the upper layer protocol from being aware of the physical medium to be used in the communication.
- D. It accepts Layer 3 packets and decides the path by which to forward the packet to a remote network.
- E. None of the above.
Answer (Click to show)
C. It shields the upper layer protocol from being aware of the physical medium to be used in the communication.
- Data link layer provides abstraction from physical media
- Handles framing, addressing, and error detection
Question Two - Fill in the Blanks
(1 Mark Each)
i. ______ is a 32-bit number used to divide an IP address into network and host portions and determine the network’s size.
Answer (Click to show)
Subnet Mask
ii. ______ is the 128-bit addressing scheme, developed to handle expansion and scalability of modern networks.
Answer (Click to show)
IPv6
iii. ______ and______ are both network communication protocols.______ ensures reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of packets, while______ is faster but does not guarantee delivery or order.
Answer (Click to show)
TCP and UDP are both network communication protocols. TCP ensures reliable, ordered, and error-checked delivery of packets, while UDP is faster but does not guarantee delivery or order.
iv. ______ is a decentralized naming system for computers, services, or any resource connected to the Internet or a private network, which translates domain names into IP addresses.
Answer (Click to show)
DNS (Domain Name System)
v.______ is the command that is used to test network connectivity between devices, but it can also be used to determine how many routers are in between a source and a destination.
Answer (Click to show)
Traceroute (or tracert on Windows)
vi. Special condition in a network where more data packets are coming to network devices than they can handle, is called ______.
Answer (Click to show)
Congestion
vii. All computers connected to the internet and wanting to use it for sending/receiving data must follow a common set of rules or guidelines for communication called______.
Answer (Click to show)
Protocols
Question Three - Short Answer
a. Briefly explain the techniques that have been used to deal with the scarcity of IPv4?
(3 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Techniques to handle IPv4 scarcity:
- NAT (Network Address Translation) - Allows multiple private IP devices to share a single public IP
- CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) - Flexible IP allocation reducing address waste
- Private IP Addresses (RFC 1918) - Reusable addresses for internal networks
- DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration) - Dynamic address assignment from pools
- IPv6 Deployment - Long-term solution with 128-bit address space
b. Differentiate between OSI and TCP/IP model.
(4 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Feature OSI Model TCP/IP Model Layers 7 layers 4 layers Development Theoretical standard by ISO Practical implementation for Internet Protocol Dependency Protocol-independent Built around TCP/IP protocols Layer Names Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, Application Network Access, Internet, Transport, Application Usage Teaching/reference model Actual Internet standard Approach Top-down Bottom-up
c. Differentiate IPv4, MAC and port addressing.
(3 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Addressing Type Layer Size Purpose Scope IPv4 Address Network (L3) 32 bits Logical network identification Global routing MAC Address Data Link (L2) 48 bits Physical device identification Local network only Port Address Transport (L4) 16 bits Application/service identification Host-specific
Question Four - IPv6 & Addressing
a. Write the value of the version control field of IPv4 and IPv6 in binary numbers.
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
- IPv4 Version Field:
0100(binary for 4)- IPv6 Version Field:
0110(binary for 6)
b. Express the IPv4 address 192.168.10.51 in IPv6 format.
(2 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
IPv4-mapped IPv6 address:
::FFFF:192.168.10.51- or
::FFFF:C0A8:0A33(hexadecimal)
c. What are the techniques that help to migrate from IPv4 to IPv6?
(3 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
IPv4 to IPv6 Migration Techniques:
- Dual Stack - Devices run both IPv4 and IPv6 simultaneously
- Tunneling - Encapsulate IPv6 packets in IPv4 for traversal through IPv4 networks
- Translation - NAT64/DNS64 for communication between IPv4 and IPv6 networks
- 6to4/4in6 Tunnels - Automatic tunneling mechanisms
d. Express the IPv6 address in a compressed format: 2001:0db8:0000:0000:0a50:0000:0000:0001
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
Compressed format:
2001:db8::a50:0:0:1- or
2001:db8:0:0:a50::1
e. Express the following IPv6 address in a standard format: 2002:420:c4:1008:25:190::990
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
Expanded format:
2002:0420:00c4:1008:0025:0190:0000:0990
f. What IP addresses does this combination isolate?
(1 Mark Each)
i. Base IP Address: 172.16.10.37 and Wildcard Mask: 255.255.255.255
Answer (Click to show)
Single host: 172.16.10.37
- Wildcard 255.255.255.255 means all bits must match exactly
ii. Base IP Address: 10.10.10.1 and Wildcard Mask: 0.0.0.0
Answer (Click to show)
Single host: 10.10.10.1
- Wildcard 0.0.0.0 means all bits must match exactly
SECTION B: (60 MARKS)
Attempt any THREE (3) out of FOUR (4) questions.
**Question Five
a. Write at least three primary differences between TCP and UDP protocols.
(3 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Feature TCP UDP Connection Connection-oriented Connectionless Reliability Reliable with ACKs Unreliable, no guarantees Ordering Maintains packet order No ordering Speed Slower due to overhead Faster, minimal overhead Flow Control Yes (sliding window) No Congestion Control Yes No Header Size 20-60 bytes 8 bytes
b. TCP protocol maintains two key dynamic values per connection: a sequence number and congestion window size.
(4 Marks)
i. Why these 2 values are important for TCP protocol?
Answer (Click to show)
Importance:
- Sequence Number: Ensures data ordering, detects duplicates/missing packets, enables retransmission
- Congestion Window: Prevents network overload, enables fair bandwidth sharing, adapts to network conditions
ii. Describe briefly how each value is computed and how is it used by TCP.
Answer (Click to show)
Sequence Number:
- Computation: Random ISN during handshake, increments by bytes sent
- Usage: Receiver ACKs sequence numbers, sender retransmits unACKed data
Congestion Window (cwnd):
- Computation: Starts small, increases on successful ACKs (slow start/congestion avoidance), decreases on packet loss
- Usage: Limits data in flight, controls sending rate
c. What is the need for the UDP? Would it not have been enough to just let user’s processes send IP packets without using a transport protocol? Explain in a few sentences.
(6 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
UDP is essential because:
- Port-based Multiplexing: Without transport layer, OS couldn’t determine which application should receive incoming packets
- Process Identification: IP only handles host-to-host delivery; UDP adds process-to-process delivery via ports
- Application Requirements: Real-time apps (VoIP, streaming) need speed over reliability
- Minimal Overhead: Some applications (DNS, DHCP) need simple request-response without TCP complexity
- Custom Protocols: Allows applications to implement their own reliability if needed
d. Explain what will happen when two applications (one using TCP, the other using UDP) that want to send as much data as possible compete for bandwidth.
(7 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Bandwidth Competition Outcome:
- TCP Behavior: Will throttle back due to congestion control mechanisms
- UDP Behavior: Will continue sending at maximum rate (no congestion control)
- Result: UDP application dominates bandwidth over time
- TCP Response: Detects packet loss → reduces congestion window → sends less data
- UDP Advantage: No backoff mechanism → consumes available bandwidth aggressively
- Network Impact: Can lead to “unfair” bandwidth allocation and TCP starvation
- Solution: Requires QoS mechanisms or fair queuing on network devices
Question Six
a. You are tasked with assigning IP addresses for your new MAN with 8 buildings; each building will have 255 workstations. Use 172.31.0.0 network. Determine:
(2 Marks Each)
i. Subnet masks
ii. Network addresses
iii. Broadcast address for each subnet
iv. Valid host ranges on each subnet
v. Reserved subnets and addresses
Answer (Click to show)
Subnetting Solution for 172.31.0.0/16:
Requirements: 8 subnets, 255 hosts each
- Host bits needed: 2^n - 2 ≥ 255 → n = 9 bits (510 usable hosts)
- Subnet mask: /23 = 255.255.254.0
Building Network Address Broadcast Host Range Usable Hosts 1 172.31.0.0/23 172.31.1.255 172.31.0.1 - 172.31.1.254 510 2 172.31.2.0/23 172.31.3.255 172.31.2.1 - 172.31.3.254 510 3 172.31.4.0/23 172.31.5.255 172.31.4.1 - 172.31.5.254 510 4 172.31.6.0/23 172.31.7.255 172.31.6.1 - 172.31.7.254 510 5 172.31.8.0/23 172.31.9.255 172.31.8.1 - 172.31.9.254 510 6 172.31.10.0/23 172.31.11.255 172.31.10.1 - 172.31.11.254 510 7 172.31.12.0/23 172.31.13.255 172.31.12.1 - 172.31.13.254 510 8 172.31.14.0/23 172.31.15.255 172.31.14.1 - 172.31.15.254 510 Reserved: Network and broadcast addresses in each range
b. Subnet the network topology using 172.30.4.0/22 space. Provide answer in table format.
(10 Marks)
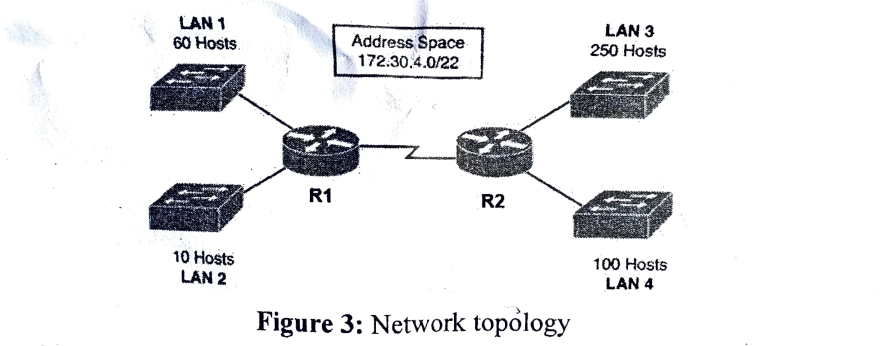
Answer (Click to show)
Note: Without specific topology diagram, here’s a general approach:
Given: 172.30.4.0/22 = 172.30.4.0 - 172.30.7.255 (1024 addresses)
Subnetting Strategy Table:
Department Hosts Needed Subnet Mask CIDR Network ID Broadcast ID Host Range IT 120 255.255.255.128 /25 172.30.4.0 172.30.4.127 172.30.4.1-126 Sales 60 255.255.255.192 /26 172.30.4.128 172.30.4.191 172.30.4.129-190 HR 30 255.255.255.224 /27 172.30.4.192 172.30.4.223 172.30.4.193-222 Admin 12 255.255.255.240 /28 172.30.4.224 172.30.4.239 172.30.4.225-238 Router Links 2 each 255.255.255.252 /30 172.30.4.240+ … … Adjust based on actual department sizes from topology
Question Seven
a. Suppose a computer has MAC address “fc:99:47:75:ce:e0”. What will be:
(5 Marks Each)
i. The LLA IPv6 address if configured with SLAAC using EUI-64 process
Answer (Click to show)
LLA Calculation Steps:
- MAC:
fc:99:47:75:ce:e0- Split:
fc:99:47|75:ce:e0- Insert
ff:fe:fc:99:47:ff:fe:75:ce:e0- Invert 7th bit:
fc=11111100→11111110=fe- Result:
fe80::fe99:47ff:fe75:cee0
ii. The GUA IPv6 address if configured with SLAAC using random generated 64-bit number
Answer (Click to show)
GUA with Random Interface ID:
- Assume network prefix:
2001:db8:1234:abcd::/64- Random IID:
a5:b3c4:1f2e:8d5b(example)- Result:
2001:db8:1234:abcd:a5:b3c4:1f2e:8d5b- Note: Random IID provides privacy, not derived from MAC
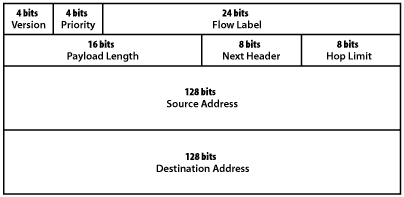
b. Draw the IPv6 packet header format and provide a brief explanation of each field in the header.
(10 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
IPv6 Header Format:
Field Explanations:
- Version (4 bits): IP version number (6 for IPv6)
- Traffic Class (8 bits): QoS prioritization (similar to IPv4 ToS)
- Flow Label (20 bits): Identifies packet flow for special handling
- Payload Length (16 bits): Length of data after header (includes extension headers)
- Next Header (8 bits): Identifies next header type (TCP=6, UDP=17, or extension header)
- Hop Limit (8 bits): Decremented by each router (replaces IPv4 TTL)
- Source Address (128 bits): Sender’s IPv6 address
- Destination Address (128 bits): Recipient’s IPv6 address
Question Eight
a. Suppose Juma, with a Web-based e-mail account, sends a message to Anna, who accesses his mail using POP3.
i. Discuss how the message gets from Juma’s host to Anna’s host.
(2 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Message Delivery Path:
- Juma → HTTP/HTTPS → Webmail Server (composes/sends email)
- Webmail Server → SMTP → Anna’s Mail Server (message transfer)
- Anna’s Mail Server stores message in her mailbox
- Anna → POP3 → Her Mail Server (retrieves message to local client)
ii. What are the series of application-layer protocols that are used to move the message between the two hosts?
(4 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Application Layer Protocols:
- HTTP/HTTPS: Juma’s browser to webmail server (message composition)
- SMTP: Webmail server to Anna’s mail server (message transfer between servers)
- POP3: Anna’s email client to her mail server (message retrieval)
b. Consider an HTTP client that wants to retrieve a Web document at a given URL. The IP address of the HTTP server is initially unknown. What transport and application-layer protocols besides HTTP are needed in this scenario?
(4 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Required Protocols:
- DNS (Application Layer): Resolves domain name to IP address
- UDP (Transport Layer): Used for DNS queries (port 53)
- TCP (Transport Layer): Used for HTTP connection (port 80/443)
Process Flow:
- Client → DNS Query (UDP) → DNS Server (get IP)
- Client → HTTP Request (TCP) → Web Server (get document)
c. Study the captured HTTP response and answer:
(8 Marks Total)
HTTP/1.1 200 OK<cr><lf>Date: Tue, 07 Mar 2008 12:39:45 GMT<cr><lf>
Server: Apache/2.0.52 (Fedora)<cr><lf>Last-Modified: Sat, 10 Dec2005 18:27:46 GMT<cr><lf>
ETag: "52663-122-a88a4e80"<cr><lf>Content-Length: 3874<cr><lf>
Content-Type: text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1<cr><lf><cr><lf>
<ldoctype html public "-//w3c//dd html 4.0 transitional//en"></lf>
<html></lf><head></lf><meta name="GENERATOR" content="Mozilla/4.79 [en] (Windows NT 5.0; U) Netscape]"></lf>
i. What operating system is running on the server?
Answer (Click to show)
Windows NT 5.0 (from the GENERATOR meta tag)
ii. When the document was last modified?
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
Sat, 10 Dec 2005 18:27:46 GMT
iii. What Webserver software is running on the server?
(2 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Apache
iv. What is the version of the webserver software?
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
2.0.52
v. Was the server able to successfully find the document or not? Justify your answer.
(2 Marks)
Answer (Click to show)
Yes, successfully found
- HTTP Status Code:
200 OKindicates successful retrieval- Content-Length shows document size (3874 bytes)
vi. How many bytes are there in the document being returned?
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
3874 bytes (from Content-Length header)
vii. What time was the document reply provided?
(1 Mark)
Answer (Click to show)
Tue, 07 Mar 2008 12:39:45 GMT (from Date header)
END OF EXAMINATION PAPER