Data Structures and Algorithms Analysis Exam - CP 213
University of Dodoma
College of Informatics and Virtual Education
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
End of Semester One University Examination for the 2023/2024 Academic Year
Course Name: Data Structures and Algorithms Analysis
Paper Code Number: CP 213
Date of Examination: 5th March, 2024
Time: 08:00-11:00
Duration: 3 Hours
Venue(s): AUDITORIUM & LRB 102
Sitting Programme(s): BSc. CS2, SE2, CNISE2, CE2, TE2, CSDFE2, IS2, MATH2 & CARRYOVER.
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This examination paper consists of TWO (2) sections with EIGHT (8) questions in FOURTEEN (14) printed pages.
- Answer all questions in Section A and THREE (3) questions in Section B.
- The total score for this examination is 100 points. Marks are allocated at the end of each question.
- ALL responses should be written in the answer book provided. Insert the examination paper into the answer book after the examination. Students should not take any examination paper(s) out of the examination room.
- All regulations guiding the administration of university examinations apply.
SECTION A: (40 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section.
Question One
Read each question carefully and choose the most correct response.
(1 Mark Each)
i. Which of the following uses the FIFO method?
A. Queue
B. Stack
C. Hash Table
D. Binary Search Tree
E. Binary Tree
ii. Linked list search complexity is …
A. O(n)
B. O(1)
C. O(log n)
D. O(log log n)
E. O(log²n)
iii. Shell sort uses …
A. merge sort
B. quick sort
C. selection sort
D. insertion sort
E. bubble sort
iv. Depth First Search is equivalent to which of the traversals in the Binary Trees?
A. Post-order Traversal
B. Level-order Traversal
C. Pre-order Traversal
D. In-order Traversal
E. Breadth-First Search
v. The Data structure used in the standard implementation of Breadth First Search is?
A. Queue
B. Linked List
C. Tree
D. Stack
E. Double Linked List
vi. Time complexity of DFS is? (V - number of vertices, E - number of edges).
A. O(V+E)
B. O(V)
C. O(E)
D. O(V*E)
E. O(V/E)
vii. Breadth First Search is equivalent to which of the traversals in the Binary Trees?
A. Pre-order Traversal
B. Post-order Traversal
C. Level-order Traversal
D. In-order Traversal
E. Depth First Search
viii. Time complexity of Breadth First Search is? (V = number of vertices, E = number of edges).
A. O(V + E)
B. O(V)
C. O(E)
D. O(V*E)
E. O(V/E)
ix. Data structure that contains a relationship between a pair of elements, this is not necessarily hierarchical in nature.
A. Tree
B. String
C. Graph
D. Array
E. Structure
x. Which of the following involves arranging the records in a logical order?
A. Merging
B. Sorting
C. Traversing
D. Searching
E. Shuffling
Question Two
Match the item in Column A with its corresponding item in Column B.
(1 Mark Each)
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| i. Combines record into different sorted files into a single file | A. Linear search |
| ii. A set of data values and associated operations that are specified accurately, independent of any particular implementation. | B. Merging |
| iii. It is not a primitive data type. | C. Edges |
| iv. A data structure that is very useful in situations when data are stored and then retrieved in reverse order. | D. Deletion |
| v. A data structure that can store the non-homogeneous data element. | E. False |
| vi. A search that starts at the beginning of the list and checks every element in the list. | F. Array |
| vii. An operation that is implemented similarly in both queue and stack. | G. Structure |
| viii. The name given to nodes in a graph. | H. Data structure |
| ix. It defines how the data item or items are logically related. | I. Abstract data type |
| x. In a linked list, Pointers stores the next data element of a list. | J. Vertices |
| K. True | |
| L. Stack | |
| M. Insertion |
Question Three
Write T for the correct statement and F for the incorrect statement.
(1 Mark Each)
i. The new keyword frees the memory allocated dynamically.
ii. Push adds items item into a stack.
iii. Infix expression has an operator between operands.
iv. Void is the type with an empty set of values.
v. Enqueue is a stack operation
vi. LIFO is a working principle of a tree data structure.
vii. Return keyword terminates the current function and returns the specified value (if any) to the caller.
viii. The size of an array is calculated by the sizeof operator
ix. /n is a newline operator
x. The delete keyword assigns a new value to memory.
Question Four
a. With the aid of a code segment, briefly describe the following programming concepts.
i. Recursive functions (2 Marks)
ii. Pointers (2 Marks)
iii. Sentinel while loop (1 Mark)
b. Show by using diagrams, how 3! is performed by computer program using: (2.5 Marks Each)
i. Iteration
ii. Recursion
SECTION B: (60 MARKS)
Attempt any THREE (3) out of FOUR (4) questions provided.
Question Five
Members from the computer programming club at the University of Dodoma were doing a computer programming challenge. A linked list of four nodes as Figure 1 was displayed to the members. Consider yourself as a member of the club, take into account the given structure definition below.
struct AttendeeCard
{
int card_no;
struct AttendeeCard * next;
};Figure 1: Singly Linked List
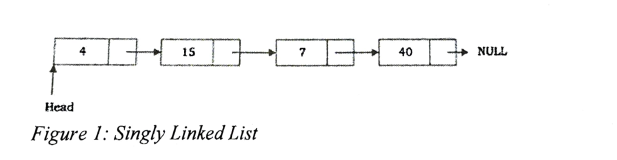
a. From the structure definition and Figure 1 (1 Mark Each)
i. State the name of a structure.
ii. How many numbers of nodes are there?
iii. How many members of the structure are there?
iv. State the data part
v. State the pointer part
b. Write a piece of code to perform the following operations on Figure 1: (Hint: use MyCard as the node name, each operation should be performed on the original Figure 1)
i. Insert a new node at the beginning of the list. (3 Marks)
ii. Insert a new node between cards with card_no 7 and 40. (3 Marks)
iii. Delete the last node. (3 Marks)
iv. Delete a card with card_no 7. (3 Marks)
v. Display all card_no stored. (3 Marks)
Question Six
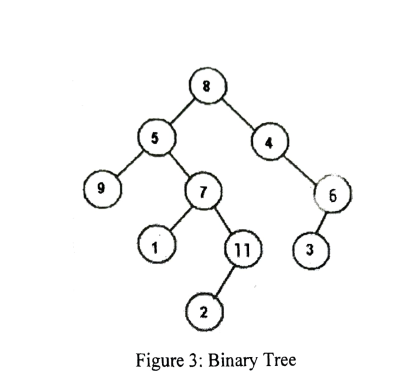
The binary tree is a graph with special characteristics that gives it distinct features from normal trees and other graphs. Figure 2 and Figure 3 gives the diagrammatical difference between a graph and a binary tree.
Figure 2: Graph
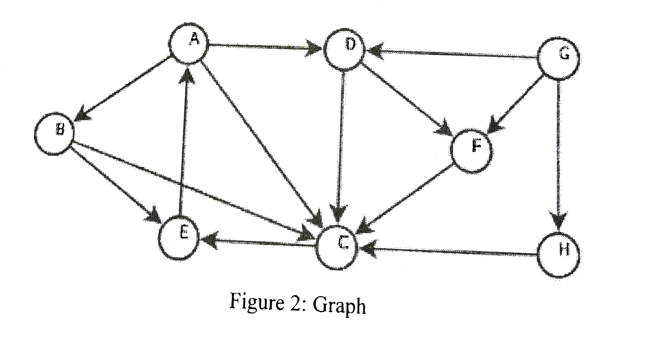
Figure 3: Binary Tree
a. Consider Figure 2 to answer the following questions:
i. Demonstrate the use of stack in performing Depth First Search (6 Marks)
ii. Demonstrate the use of queue in performing Breadth First Search (6 Marks)
b. Consider Figure 3 to state:
i. Level order traversal (2 Marks)
ii. In-order traversal (2 Marks)
iii. Post-order traversal (2 Marks)
iv. Pre-order traversal (2 Marks)
Question Seven
Given array A as shown Figure 4, answer the question that follows.
Figure 4: Unsorted array
| data | 67 | 45 | 36 | 78 | 90 | 40 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
a. Show diagrammatically how the Merge sort algorithms sorts the array A in ascending order. (5 Marks)
b. If 56 is taken as pivot (piv = A[high]) and lower bound (lb) and upper bound (ub) are set to lb = A[low]; and ub = A[high] respectively. Using the partition pseudocode of quick sort given below.
partition(A[], low, high)
{
//pivot (Element to be placed at right position)
piv = A[high];
//index of smaller element
i = (low -1);
for(j = low; j < high-1; j++)
{
//if the current element is smaller than or equal to pivot
if(A[j] <= piv)
{
//increment index of smaller element
i++;
swap a[i] and A[j]
}
}
swap A[i+1] and a[high]
return (i + 1)
}Show:
i. The value of the lower bound (lb) and the upper bound (ub) when the first swap will have to take place. (3 marks)
ii. The value of the lb and ub when the second swap will have to take place. (3 marks)
iii. The return value of the code. (2 marks)
c. Write a piece bubble sort code to sort the array A in descending order. (7 marks)
Question Eight
Queue and stack data structure have various technical application in our daily life. Consider Figure 5 which indicate a four node linked list created from the given structure definition below, and the node name as Student.
struct StudentWeight
{
float weight;
StudentWeight * next;
}Figure 5: Linked list with 4 nodes
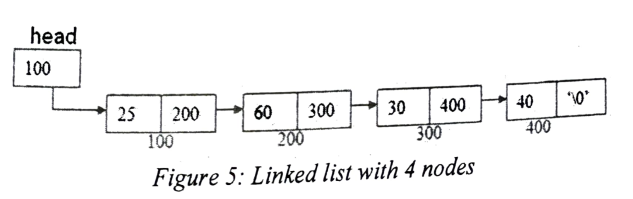
a. Assume Figure 5 is a stack;
i. Write a piece of code to push two students weighted 91 and 56. (3 Marks)
ii. If after an operation in 8(a)(i) the two nodes take addresses 500 and 600 respectively, sketch the resultant stack. (2 Marks)
b. Assume Figure 5 is a queue;
i. Write a piece of code to enqueue two students weighted 94 and 17. (3 Marks)
ii. If after an operation in 8(b)(i) the two nodes take addresses 500 and 600 respectively, sketch the resultant stack. (2 Marks)
c. Using stack concept, show each step you will pass to respond to the following questions.
i. Convert the following infix expression into postfix A * (B + C * D) + E (4 Marks)
ii. Evaluate the following postfix expression 22842 - / * + 10 - (4 Marks)
d. Find the values of the following expressions. (1 Mark Each)
i. 512 + 4 * + 3 -
ii. + - * 22 / 1685
END OF EXAMINATION PAPER