Object Oriented Programming Exam - CP 215
THE UNIVERSITY OF DODOMA
COLLEGE OF INFORMATICS AND VIRTUAL EDUCATION
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
End of Semester One University Examination for the 2022/2023 Academic Year
Course Name: Object Oriented Programming in Java
Paper Code Number: CP 215 UE
Date of Examination: 27th February, 2023
Duration: 3 Hours
Sitting Programme(s): BSc.BIS2, MTA, HIS2, DCBE2, IDIT2
INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
i. This examination paper consists of TWO (2) sections with a total of SEVEN (7) questions. ii. Answer all questions in Section A and THREE (3) questions in Section B. iii. The total score for this examination is 100 points. Marks are allocated at the end of each question. iv. ALL responses should be written in the answer book provided. v. Insert the examination paper into the answer book after the examination. vi. Students must not take any examination paper(s) out of the examination room. vii. All regulations guiding the administration of university examinations apply.
SECTION A: (40 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section.
Question One: Multiple Choice (10 Marks)
Read each question carefully and choose the most correct response. (1 Mark Each)
i. The static variable declared in a class is called ;
A. Local Variables
B. Class variables
C. Instance variables
D. Object variables
E. Global variables
ii. Which of the following characteristics of an object-oriented programming language restricts behaviour so that an object can only perform actions that are defined for its class?
A. Dynamic Binding
B. Polymorphism
C. Inheritance
D. Encapsulation
E. Abstraction
iii. Which command lines will compile and run a java class called echo respectively?
A. javac echo and java echo.java
B. javac echo.java and java echo
C. java echo.class and javac echo
D. java echo and javac echo.java
E. javac echo.java and java echo.class
iv. What type of relationship exists between myMethod in class Animal and myMethod in class Dog?
class Animal {
public void myMethod ( ) {
System.out.println("from class Animal");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
public void myMethod( String x ) {
System.out.println("from class Dog: " + x );
}
}A. Method overloading
B. Method hiding
C. Method binding
D. Method Overcoming
v. Which of the following statement describes dynamic resizing as it applies to the ArrayList class?
A. The size of a new ArrayList object must be specified at instantiation.
B. The size of an ArrayList object can be iterated throughout a program.
C. The size of an ArrayList object is fixed at instantiation.
D. The object changes size dynamically as new elements are added.
E. Both A and B
vi. Assume you have three classes: Person, Teacher, and Student. Teacher and Student are both subclasses of Person. The Person class has a method called getDetails(). If a Teacher object is stored in a Person variable, which getDetails() method is called?
A. Always the Person class’s method.
B. Always the Teacher class’s method.
C. The method from the class used to declare the variable.
D. The method from the class used to create the object.
vii. Which of the following statement is true?
A. X extends Y is correct if and only if X is a class and Y is an interface
B. X extends Y is correct if and only if X is an interface and Y is a class
C. X extends Y is correct for all combinations of X and Y being classes and/ or interfaces
D. X extends Y is correct if X and Y are either both classes and both interfaces
E. Both C and D
viii. The following are examples of checked exceptions EXCEPT?:-
A. SQLException
B. IOException
C. RunTimeException
D. ClassNotFoundException
E. InputMismatchException
ix. What is known by the declaration ArrayList list = new ArrayList();?
A. list is an ArrayList object.
B. Elements of the list array are objects.
C. The type of information stored by list is unknown.
D. The number of array elements is not specified.
E. All of the above
x. Which statement about interfaces is true?
I. An interface contains only public abstract methods and public static final fields.
II. If a class implements an interface and then fails to implement any methods in that interface, then the class must be declared abstract.
III. While a class may implement just one interface, it may extend more than one class.
A. I only
B. I and II only
C. I and III only
D. II and III only
E. I, II, and III
Question Two: Matching (10 Marks)
Match the item in Column A with its corresponding item in Column B. (1 Mark Each)
| Column A | Column B |
|---|---|
| i. Identify and discard objects that are no longer needed by a program | A. int, double, Float |
| ii. The method must have access specifier at least that of the parent class, and return type, name and identical parameter list. | B. abstract |
| iii. Examples of wrapper classes | C. Encapsulation |
| iv. It is always invoked when a new object is created. | D. final class |
| v. The base class of unchecked exception. | E. Inheritance |
| vi. Prevent anyone from instantiating the class directly. | F. Collection of abstract class |
| vii. Cannot be extended | G. Class |
| viii. The mechanism allows printf() and println() methods to invoke toString() method automatically. | H. Double, Integer, Character |
| ix. Blueprint or template of an object. | I. Object |
| x. Private members, getter and setter methods. | J. Garbage collection |
| K. Composition | |
| L. Overriding | |
| M. Enhanced for loop | |
| N. ArrayList class | |
| O. Error | |
| P. Specialization | |
| Q. Instance of class | |
| R. RuntimeException | |
| S. Late binding | |
| T. Polymorphism | |
| U. Collection of abstract methods | |
| V. Overloading | |
| W. Constructor | |
| X. Interface |
SECTION B: (60 MARKS)
Answer any THREE (3) questions from this section.
Question Three (12 Marks)
(a) Why is the main method declared static? (2 Marks)
(b) Briefly explain how add(index, values) affects the performance of a Java collection? (2 Marks)
(c) Carefully read the following program and use it to answer questions that follow. Comments indicate where missing components are to be placed. (2 Marks Each)
public class MyMain {
public static void main(String []args){
//(2)print the greeting
//(3)construct a MyClass object called myObject
//(4) update()
}
}
class MyClass{
// (1) definition of MyClass constructor
public static void greetings(){
// definition of greets
}
public void update(int num, String title){
// definition of update
}
public void print(){
// definition of print
}
private int numOfItems;
private String reportTitle;
}i. Write a statement that will construct a MyClass object called myObject at line (3).
ii. Write a statement that will call the method that prints the greeting, at line (2).
iii. Write a statement that will call the update method at line (4).
Question Four (20 Marks)
Create a class called Book with the following attributes: ISBN (int), title (String), author (String), and price (double). Include a constructor, getter and setter methods for all attributes, and a toString method for returning its string representation. Include a main method to test your application. (20 Marks)
Question Five (20 Marks)
Figure 1 shows a schematic representation of Payable interface, Invoice, Employee and SalariedEmployee classes.
Figure 1: Relationship between interface Payable, class Invoice, Employee and Salaried Employee.
Use the following information to write an application to determine payments for employees and invoices. You are required to create interface Payable, which contains method getPaymentAmount that returns a double amount that must be paid for an object of any class that implements the interface. Method getPaymentAmount is a general-purpose method to be implemented by classes that implements interface Payable. After declaring Payable interface, define class Invoice and Employee, such that they implement interface Payable. Classes Invoice and Employee both represent things for which the company must be able to calculate a payment amount. Both classes implement the interface Payable, so that a program can invoke method getPaymentAmount on Invoice objects and Employee objects. Class Invoice represents a simple invoice that contains billing information for only one kind of part. The class declares private instance variables partNumber, partDescription, quantity and pricePerItem. Class Invoice also contains a constructor, get methods and a toString method that returns a String representation of an Invoice object. The class Employee contains employee’s firstName, lastName, and employeeID. It also contains a constructor for initialization of instance variable and a toString method for returning its string representation. Salaried employee is paid a fixed weekly salary regardless of the number of hours worked. Therefore, SalariedEmployee class should contain a unique variable called salary, a constructor, a toString method for returning its string representation. Include main method to test your application. (20 Marks)
Question Six (20 Marks)
(a) Java collection framework provides wrapper classes that enable programmer to store primitive data type values as objects. Use appropriate wrapper class, write a program that reads a list of grades from the keyboard in the range 0 to 100. The program should prompt the user with “Please enter a grade between 0 to 100 or -1 to quit” each time before reading the next grade. Store each grade in its corresponding ArrayList (A, B, C, D or F) as follows: 90 to 100 = A, 80 to 89 = B, 70 to 79 = C, 60 to 69 = D, and 0 to 59 = F.
Your program should output the total number of grades entered on each array list. For example, if the inputs is: 38 86 92 55 83 42 90 -1, each on separate line then the output will be:
Total number of grades = 7
Number of A = 2
Number of B = 2
Number of C = 0
Number of D = 0
Number of F = 3.
Note that the grade may include decimal points and include appropriate packages.(8 Marks)
(b) Suppose you have two sorted lists:
- ListA = [1, 4, 8, 9, 11, 15, 17, 28, 41, 59]
- ListB = [4, 7, 11, 17, 19, 20, 23, 28, 37, 59, 81]
Write a program that performs the following tasks:
i. Overload a method add() to add elements to each ArrayList. (3 Marks)
ii. Include a method intersect that accepts two sorted array lists of integers as parameters and returns a new list that contains only the elements found in both lists. (3 Marks)
iii. Include a method union that accepts two sorted array lists of integers as parameters and returns a new list that contains all elements found in either list (without duplicates). (3 Marks)
iv. Include a main method to test your application. Use the Iterator class to print elements from the lists. (3 Marks)
Question Seven (20 Marks)
(a) Consider the classes Student and Address. Every student has an address, therefore the relationship between student and address is a Has-A relationship. But if you consider it in the reverse, the address does not contain a student. Write three java classes to implement this relationship. Note that Address may contain street number, city and country while student class may have student address, name and id. The third class should contain main method to test your application. (8 Marks)
(b) Suppose you have the following relational schema on your localhost MySQL database named CompanyData:
- Emp(eid: int, ename: varchar(45), DoB: varchar(30), salary: float)
- Works(eid: int, did: int, pct_time: int)
- Dept(did: int, dname: varchar(30), budget: float, managerid: int)
Write a program that will:
- Establish a JDBC connection to the database.
- Add a Sex column to the Employee (Emp) table.
- Ensure that the values for this new column are properly handled.
(12 Marks)
Question Eight
Figure 1 shows a schematic representation of Payable interface, Invoice, Employee and SalariedEmployee classes.
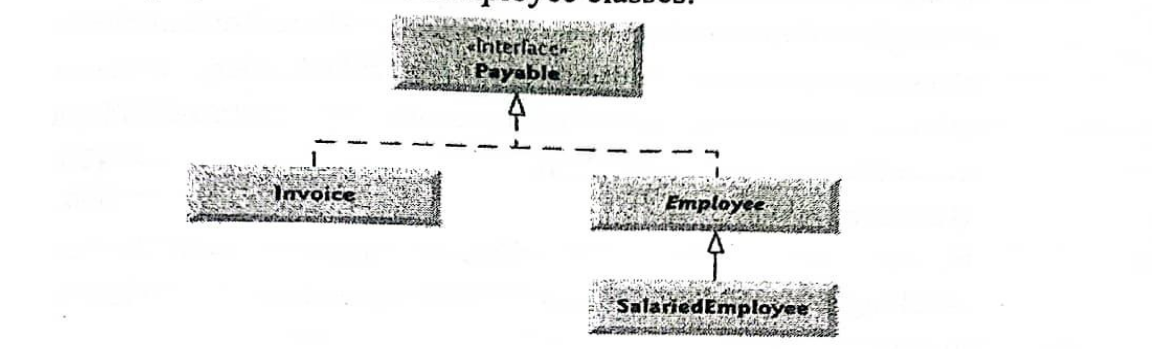
(Figure 1: Relationship between interface Payable, class Invoice, Employee and SalariedEmployee.)
Use the following information to write an application to determine payments for employees and invoices. You are required to create interface Payable, which contains method getPaymentAmount that returns a double amount that must be paid for an object of any class that implements the interface. Method getPaymentAmount is a general-purpose method to be implemented by classes that implements interface Payable. After declaring Payable interface, define class Invoice and Employee, such that they implement interface Payable. Classes Invoice and Employee both represent things for which the company must be able to calculate a payment amount. Both classes implement the interface Payable, so that a program can invoke method getPaymentAmount on Invoice objects and Employee objects. Class Invoice represents a simple invoice that contains billing information for only one kind of part. The class declares private instance variables partNumber, partDescription, quantity and pricePerItem. Class Invoice also contains a constructor, get methods and a toString method that returns a String representation of an Invoice object. The class Employee contains employee’s firstName, lastName, and employeeID. It also contains a constructor for initialization of instance variable and a toString method for returning its string representation. Salaried employee is paid a fixed weekly salary regardless of the number of hours worked. Therefore, SalariedEmployee class should contain a unique variable called salary, a constructor, a toString method for returning its string representation. Include main method to test your application.
(20 Marks)
END OF EXAMINATION PAPER